Massage, as one of the traditional therapies of traditional Chinese medicine, plays an important role in regulating the body, relieving pain and promoting health with its unique theoretical system and rich practical experience. The basic operating skills of massage techniques are the core abilities that every massage therapist must master. It is not only related to the treatment effect, but also directly affects the patient’s comfort and safety. The following will elaborate on the basic operational skills of massage techniques, including preparations, basic techniques, operating points and precautions.

1. Clear fitness goals
1. Environment preparation
Massage therapy should be performed in a quiet, warm, and well-ventilated environment to reduce external interference and keep the patient relaxed. The indoor light is soft, avoiding direct glare and creating a comfortable treatment atmosphere. At the same time, ensure that the treatment bed or chair is stable and comfortable, making it convenient for the patient to lie down or sit up, and for the massage therapist to operate.
2. Patient preparation
Before treatment, the patient’s medical history, allergy history and current physical condition should be understood in detail to assess whether the patient is suitable for massage therapy. Instruct patients to wear loose, comfortable clothing that will facilitate exposure of the treatment area. For female patients, pay attention to protecting privacy and use screens or curtains if necessary. In addition, inform the patient of possible feelings during the massage process, such as soreness, swelling, warmth, etc., to eliminate their nervousness.
3. Masseur preparation
Masseurs should dress neatly, trim their nails, and avoid wearing jewelry to prevent scratching the patient’s skin. Wash your hands before operation. If necessary, apply an appropriate amount of lubricant (such as massage oil, ointment, etc.) to reduce friction and improve the treatment effect. At the same time, massage therapists need to maintain a good mental state and concentrate to ensure the accuracy and effectiveness of massage techniques.
2. Basic techniques
There are many types of massage techniques, but they can be summarized into several basic categories, including pressing, rubbing, pushing, kneading, kneading, rubbing, shaking, tapping, etc. Each technique has its specific action site, operation methods and effects.
1. Press the method
The massage method is one of the most basic massage techniques. Pressing acupoints or muscles with fingers, palms or elbows can achieve the purpose of dredging meridians, promoting qi and blood circulation. During operation, vertical force should be applied, from light to heavy, and gradually penetrate, so that the patient feels local soreness or warmth. Be careful not to use excessive force to avoid injury.
2. Mofa
The massage method is to use the fingertips or palms to make gentle circular movements on the body surface to generate heat and promote local blood circulation. The massage method is suitable for all parts of the body, especially for areas with delicate skin or thin muscles, such as the face, abdomen, etc. During operation, the movements should be even and continuous with moderate strength so that the patient feels comfortable.
3. Push method
The pushing method is to use your fingers, palms or elbows to push muscles or meridians in a straight line in a certain direction, which has the effect of dredging meridians, regulating tendons and rehabilitating muscles. The pushing method can be divided into various forms such as direct pushing, divided pushing, combined pushing, etc. The operation should be carried out along the direction of the muscles or meridians, with even force and moderate speed, and avoid being harsh and rough.
4. Kneading method
The kneading method is to use your fingers, palms or forearms to gently rotate and knead on the body surface to produce a warm feeling in the treated area, achieving the effects of relaxing muscles and activating collaterals, activating blood circulation and removing blood stasis. The kneading method is suitable for all parts of the body, especially for areas with muscle tension and stiffness. During operation, the movements should be continuous and gentle, and the force should penetrate into deep tissues.
5. Other techniques
Kneading, rubbing, shaking, shooting and other techniques each have their own unique application scenarios and effects. For example, kneading is suitable for the thick muscles of the limbs, which can relieve muscle fatigue; rubbing can enhance local blood circulation and is suitable for limbs and The waist and back; shaking method is mostly used to relax the limbs and promote blood circulation; patting method can invigorate yang energy and promote the circulation of qi and blood.
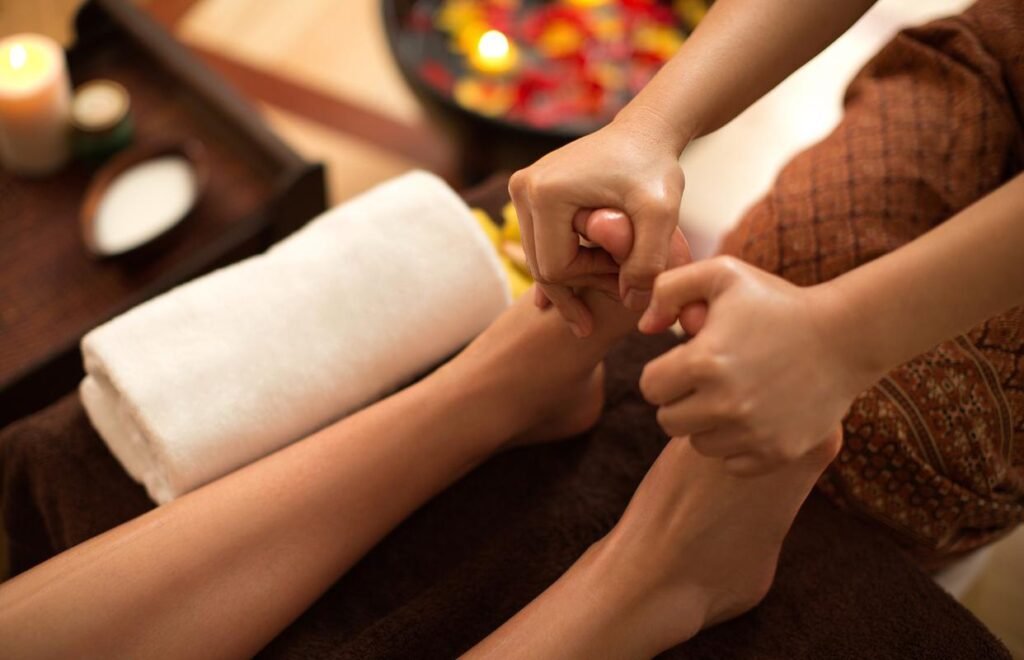

3. Operational points and precautions
1. Key points of operation
Moderate intensity: The intensity of massage should be flexibly adjusted according to the patient’s constitution, condition and tolerance, so as to achieve the therapeutic effect while avoiding damage.
- Clear direction: Massage should be performed along the direction of the muscles or meridians, and avoid reverse operations to avoid aggravating symptoms.
- Even Rhythm: Massage movements should have a steady rhythm and even intensity, avoiding being fast and slow, light and heavy.
- Coherence of techniques: Various techniques should be connected naturally, smoothly and coherently to form an overall therapeutic effect.
2. Precautions
Avoid massage on an empty stomach or on a full stomach: Massage on an empty stomach may cause hypoglycemia, while on a full stomach it may affect digestive function.
- Pay attention to the patient’s reaction: During the massage process, you should pay close attention to the patient’s reaction. If you feel uncomfortable, stop immediately, ask the patient how he feels, adjust the technique or stop the treatment.
- Protect patient privacy: During the treatment process, patient privacy should be respected and non-treatment parts should be avoided.
- Contraindications: Massage therapy should be avoided for patients with fractures, skin damage, acute inflammation, bleeding tendency, etc.